Exploring Rare Earth Elements: Their Importance and Extraction Methods
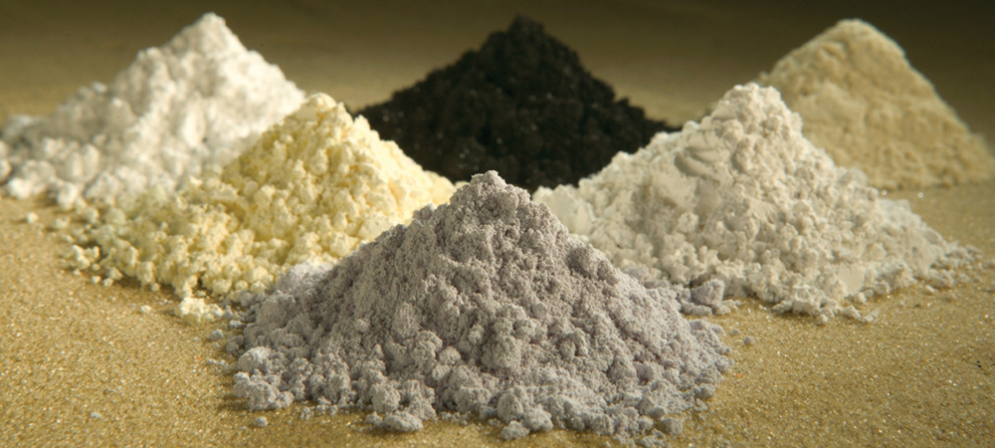

Introduction to Rare Earth Elements
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar elements, including scandium, yttrium, and the 15 lanthanides. These elements are crucial for various high-tech applications due to their unique magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties. Despite their name, rare earth elements are relatively abundant in the Earth's crust but are rarely found in concentrated and economically exploitable forms.
Extraction Methods: Mining and Processing Techniques
The Significance of Rare Earth Elements in Modern Technology
REEs are indispensable in the production of many modern technologies. They are used in the manufacturing of powerful permanent magnets, batteries, catalysts, and phosphors, which are essential components in electric vehicles, wind turbines, smartphones, and various other electronics. The growing demand for green technologies and advanced electronics underscores the critical role of REEs in driving technological innovation and sustainable development.
Global Distribution and Key Sources of Rare Earth Elements
The global distribution of REEs is uneven, with significant deposits found in countries like China, the United States, Australia, and Russia. China dominates the global REE market, accounting for the majority of production and refining capacity. Other notable sources include the Mountain Pass mine in the USA, the Mount Weld mine in Australia, and the Lovozero deposit in Russia. Understanding the geographical distribution of REEs is vital for strategic resource management and supply chain security.
Rare Earth Elements in the Middle East
The Middle East is increasingly recognized for its potential in rare earth element resources. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Jordan are investing in the exploration and development of REEs to diversify their economies beyond oil. The strategic location of the Middle East, coupled with significant investment in mining infrastructure, positions the region as an emerging hub for REE production. Collaborative efforts among Middle Eastern nations can enhance regional expertise, fostering sustainable and efficient REE extraction practices.
Rare Earth Elements in Iran
Iran's geological diversity not only includes vast oil and gas reserves but also encompasses a wealth of mineral resources, including significant deposits of rare earth elements (REEs). The country's terrain spans from deserts to mountains, providing a rich geological tapestry ripe for exploration and extraction. Historically, Iran has been recognized for its mineral wealth, which includes substantial reserves of iron ore, copper, zinc, and rare earth elements such as lanthanum, cerium, and neodymium.
Despite its geological potential, Iran's mining industry faces several challenges that impact its ability to fully exploit its rare earth element resources. International sanctions have historically hindered the country's access to advanced technologies and foreign investments necessary for efficient mining operations and processing facilities. These sanctions have limited Iran's ability to develop its mining infrastructure and adopt modern extraction techniques, thereby affecting the competitiveness of its mineral sector on the global stage.
However, Iran has been resilient in its pursuit of developing its mining capabilities. The country has invested in research and development of advanced extraction technologies and beneficiation processes to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of REE extraction. Iranian researchers and engineers have been actively collaborating with international partners to leverage expertise and innovations in mining and metallurgy, aiming to overcome technological barriers and increase the economic viability of rare earth element projects.
Moreover, Iran's strategic location and extensive mineral resources place it in a favorable position to cater to regional and global demands for rare earth elements. By strategically investing in its mining sector and fostering international partnerships, Iran aims to diversify its economy and reduce its dependency on oil revenues. The Iranian government has prioritized the development of the mining industry through legislative reforms and incentives to attract foreign investments, aiming to create a conducive environment for sustainable growth and development in the sector.
The extraction of REEs involves several complex steps, including mining, beneficiation, and refining.
Mining: REEs are extracted from ore deposits using traditional mining methods such as open-pit or underground mining. The choice of method depends on the ore's depth and geographical conditions.
Beneficiation: This process involves crushing, grinding, and separating the REEs from the ore using techniques like flotation, magnetic separation, and gravity separation.
Refining: The concentrated REEs are subjected to various chemical processes to remove impurities and isolate individual elements. This stage is highly complex due to the similar chemical properties of REEs.
Environmental and Economic Challenges in Rare Earth Element Extraction
Extracting REEs poses significant environmental and economic challenges. The mining and refining processes generate substantial waste and can lead to soil and water contamination if not managed properly. Economically, the fluctuating prices of REEs and the high cost of extraction and processing can affect project viability. Additionally, the geopolitical landscape, particularly the reliance on a few countries for supply, adds another layer of complexity to the market.
Innovative Technologies for Sustainable Extraction
Advancements in technology are paving the way for more sustainable and efficient REE extraction methods. Innovations such as bioleaching, which uses microorganisms to extract metals from ores, and solvent extraction techniques that reduce chemical waste, are gaining traction. The development of more efficient recycling processes for REEs from electronic waste also holds promise for reducing dependence on primary sources and minimizing environmental impact.
Case Studies: Successful Rare Earth Element Projects
Several projects worldwide exemplify successful REE extraction and processing. The Bayan Obo mine in China is one of the largest and most significant sources of REEs, demonstrating efficient large-scale production. In Australia, the Mount Weld mine has implemented advanced processing techniques to enhance yield and reduce environmental footprint. These case studies highlight best practices and innovative approaches that can be emulated globally.
The Future of Rare Earth Elements: Trends and Predictions
The future of REEs looks promising, driven by the increasing demand for renewable energy technologies and advanced electronics. Trends indicate a shift towards more sustainable extraction practices and the diversification of supply sources to reduce geopolitical risks. The development of new technologies and recycling methods will play a crucial role in meeting future demand and ensuring the long-term availability of these critical elements.
WE ARE KIMIA
Kimia Holding stands as a diversified conglomerate with a strong foothold in various sectors including mining and mineral resources, tourism services, livestock and poultry, agriculture, and foreign trade foreign trade in Iran and across the Middle East. However, it is within the realm of mining that Kimia Holding has truly distinguished itself, garnering recognition for its unwavering commitment to excellence and innovation.
CONTACT KIMIA
Our experts at Kimia Holding eagerly await your inquiries and are prepared to provide insightful answers or address any questions you may have. Should you require further details or wish to share your opinions, please don't hesitate to reach out. Your engagement is valuable to us.
Adherence to regulatory frameworks and industry standards is essential for responsible REE extraction. International guidelines, such as those set by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and various national regulations, ensure that mining activities are conducted safely and sustainably. Companies must navigate these regulatory landscapes to maintain compliance and secure social license to operate.
Regulatory Frameworks and Industry Standards
Resources
Conclusion: Balancing Demand with Sustainability
Rare earth elements are vital to modern technology and sustainable development. While their extraction poses significant challenges, advancements in technology and sustainable practices offer promising solutions. By balancing the growing demand for REEs with environmental stewardship and strategic resource management, the mining industry can continue to support technological innovation while protecting ecosystems for future generations.
Written by Zamin Kavan Company,
ZKC is a subsidiary of Kimia Holding, specializes in the exploration, exploitation, and processing of diverse mineral resources. It is prepared to offer technical and engineering services to stakeholders in the mining industry, encompassing consultation, design, and implementation phases. Leveraging state-of-the-art technologies and expert teams, the company has successfully completed numerous projects, significantly contributing to the development of the mining industry in the country.





