Iran's Rich Geological Survey and Mineral Exploration
Iran's rich geological survey and mineral exploration efforts represent a journey into the heart of the earth, where geologists and explorers seek to unravel the mysteries of its geological past and unlock the potential of its mineral wealth. Through systematic geological surveys, advanced mapping techniques and innovative exploration methods, Iran is paving the way for sustainable economic growth and development by harnessing its natural resources.
In this article it is aimed to discuss Iranian geology and its potential for the mineral resources development. Beginning from the mountain ranges to the deserts, we will look at the geological formations beneath and efforts being made to explore them. This exploration includes some of the most valuable minerals in Iran including iron ore, copper, zinc, and rare earth metals. Also, we will talk about the government policy and activity in relation to mineral exploration, the goals and the work of the geological survey and the outlook for a mineral exploration in the said country. Taking these aspects into consideration, one can acknowledge the ways Iran is trying to become one of the major players in the world mining industry and how its devotion to science, technology, and innovation helps to reveal its geological potential for the further generations.
Iran's Geological Diversity
Iran's geological diversity is a testament to its complex geological history, which spans millions of years and includes numerous tectonic and volcanic activities. The country's topography is marked by several prominent geological features, including the Alborz and Zagros mountain ranges, the Central Iranian Plateau, and the vast Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut deserts. Each of these regions tells a unique story of Iran's dynamic geological past.
The Alborz Mountains is in the northwest extending to northeast and is composed mostly of sedimentary and volcanic rocks of the Mesozoic era. This mountain range is made up of high mountains and some of the prominent ones are Mount Damavand which is a volcanic mountain also considered to be the highest in Asia. The formation of the Alborz has indeed been attributed to the tectonic and folding activity on account of the Arabian and Eurasian plates. This collision has also featured in the development of mineral resources especially those of the region.
In the Southwest, the region includes the Zagros Mountains which are made of folded and faulted sedimentary rocks of Cenozoic time. This mountain range is part of one of the most seismically active regions on the planet Yet, the process of tectonic convergence between the Arabia and Eurasian plates persists to this day. The Zagros area contains large reserves of oil and there are many fields especially in the foothills of the Zagros mountains. Due to these movements, it has been able to extrude various deposits like copper, zinc, as well as iron ores.
It is situated between the Alborz and Zagros mountain ranges and the Central Iranian Plateau and a great amount of difference in the structure of this area can be observed. Tectonically and volcanically, this region is not very dormant as evidenced by the presence of a number of old and extinct volcanoes in the region. This region also holds massive deposits of other minerals such as industrial minerals like gypsum, feldspar and barite among others. Within the Iranian plateau the two large deserts are Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut, the later noted for its surface features such as salt pans, sand dunes, and yardangs and kaluts shaped by agents of erosion like wind and water over millions of years.
The tectonic movement and other geological activities that have taken place in and around Iran have not only contributed in the formation of its various terrains but have also endowed the country with Australia’s deposit of minerals and ores. The fact is that this geological factor is beneficial: in this context, it is possible to study the nature, develop industries, and employ the minerals and other resources that are to be found in the habitat without negatively impacting the latter.
Key Mineral Resources of Iran
Iran’s mineral resources are greatly as equivalent to the country’s geological structures meaning it is a world-class mining nation. Such mineral resources are spread across the country’s different geological terrains, where each provides a combination of minerals that are valuable in industries among them being.
Copper is among those minerals that are the most identified and has the highest economic value in Iran. The main reserves of copper are discovered in the central and southern part of the country with primary focus in Kerman Province. Sarcheshmeh and Sungun are two among the largest mines in Iran which are specialized in copper and supply a great deal of the nation’s economy. These deposits are therefore due to massive hydrothermal activities accompanied with volcanism and tectonically active region. The last but not the least, there is also Zinc, which is also vital for Iran and the proved reserves are explored in Zanjan and Yazd Districts. Angouran mine located in Zanjan is one of the largest zinc mines of the Middle East. Iranian zinc mineralization mainly occurs in close association with the lead deposits and therefore the nature of both the metals is expected to be in the form of complex sulfide ores. These minerals are also used for different purpose such as galvanizing, making alloys, and manufacturing of battery among others. Iran also has large resources of iron ores mainly situated in the middle and the northeastern area of Iran. Chadormalu and Gol-e-Gohar iron ore mines are two of the biggest iron ore mining industries amongst all those in Iran, and they export millions of tones iron ore every year. These deposits are most closely linked with Precambrian plus Paleozoic rock types, meaning they are geologically very old. Still, along with these primary minerals, Iran is also endowed with rare earth minerals, the importance of which has recently come into focus because of electronics, renewable sources of energy, and electric vehicles. These elements are applied in the manufacturing of electronics, renewable energy solutions, and automobile technology that focused on electric vehicles. Iran’s rare elements deposit has been established to be mainly in the central and eastern parts and has been found to be genetically connected to the alkaline or carbonatite complexes. The procurement and treatment of them involve high-tech as well as green techniques because of the geochemical character and capabilities to harm the environment.
Iran boasts substantial iron ore reserves, making it a prominent player in the global mining industry. The exploration of Iran's iron ore deposits involves extensive geological surveys and the application of advanced exploration techniques. These activities have led to the identification of significant iron ore reserves across various regions of the country, including Kerman, Yazd, and Isfahan.
Prospecting involves conducting a geophysical study besides ground checking in order to locate the probable iron ores. The remote sensing technologies as well as magnetic, gravity, and seismic surveys are adopted by geologists to establish indications of iron ores. Once potential sites have been identified, then intensive sampling and drilling is done to determine the quality and quantity of the ore-bearing material, through various exploration drilling programs which offer important data on the ore body’s depth, thickness and its grade, important factors in determining the viability of mining operations on any given site.
Among the countries, Iran also possess some of the largest iron ore deposits which are located in Kerman Province where one of the biggest is the Gol-e-Gohar iron ore deposit. It contains six principal accumulated loads, which, with the overall anticipated amount of over 1,000 million tons, makes it one of the Central Asian republics’ largest deposits. 1 billion tons. The Gol-e-Gohar’s non-coking high-grade magnetite iron ore is mined through conventional open cast methods and Richard’s fractions and pelletized iron concentrate. In the same manner the Chadormalu iron ore mine in the Yazd Province is also another large mine with estimated resource in excess of 400 Million tons. The ore found at Chadormalu is hematite and magnetite and the mining carried out here is both through the techniques of opencast and underground.
In the Sangan iron ore mines of Isfahan Province the deposits are reported to be enormous, extent to which is calculated to be at least 1.2 billion tons of ore Sangan, due to its proximity to large population and exists infrastructure, is considered to be Iran’s important iron ore producing region. This resource is used in the production of steel as concentrate and pellets from the Sangan’s ore.
Current exploration activities carried out by Iran are partly funded through capital investments in the mining industry. The state or governmental organizations such as the Iranian Mines and Mining Industries Development and Renovation Organization (IMIDRO) are involved in supporting and subsidizing the exploration ventures. Such plans and programs give directions and focus on improving the methods of extraction and proper management of iron ores.
With its abundant iron ore reserves, Iran is well-positioned to meet domestic steel industry demands and expand its presence in the international market. The country's focus on modernizing its mining infrastructure and adopting advanced technologies will further bolster its capabilities in iron ore exploration and production.
Mineral Exploration of Iron Ore
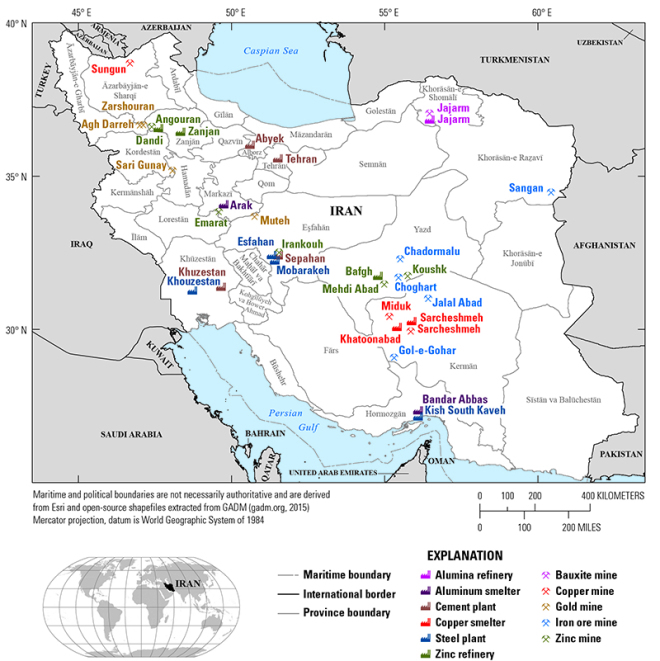
Mineral resources in Iran play an important role in its economic growth and have a significant strategic place worldwide. This means that the country can develop technologically and remain economically stable by exploiting these resources sustainably and efficiently. For Iran to benefit fully from its mineral wealth, therefore, it is necessary to continue with exploration and investment in mining infrastructure.
Illustrated map of Iran showing various mining sites and refining/smelting plants of nonfuel minerals
WE ARE KIMIA
Kimia Holding stands as a diversified conglomerate with a strong foothold in various sectors including mining and mineral resources, tourism services, livestock and poultry, agriculture, and foreign trade foreign trade in Iran and across the Middle East. However, it is within the realm of mining that Kimia Holding has truly distinguished itself, garnering recognition for its unwavering commitment to excellence and innovation.
CONTACT KIMIA
Our experts at Kimia Holding eagerly await your inquiries and are prepared to provide insightful answers or address any questions you may have. Should you require further details or wish to share your opinions, please don't hesitate to reach out. Your engagement is valuable to us.
Objectives of GSI and Mapping
One of the key objectives of Iran's Geological Survey and Mapping efforts is to produce accurate and detailed geological maps that provide valuable insights into the nation's geological composition, structure, and history. These maps serve as essential tools for identifying potential mineral resources, assessing geological hazards and planning land use activities. Through the use of advanced technologies such as remote sensing, geographic information systems (GIS) and satellite imagery, the GSI is able to create high-resolution geological maps that cover vast areas of the country.
Geological maps are crucial for various sectors, including mining, construction, agriculture, and environmental management. They help identify areas rich in minerals, guide infrastructure development, and assist in disaster risk reduction by highlighting zones prone to earthquakes, landslides, and floods. For instance, detailed geological mapping has facilitated the discovery and development of significant mineral deposits such as the iron ore reserves in Kerman and Yazd, contributing to Iran’s economic growth.
In addition to geological mapping, the GSI is actively engaged in mineral exploration activities aimed at identifying and assessing the nation’s mineral resources. These efforts involve systematic prospecting, sampling and drilling activities in areas of known mineralization, as well as in regions with potential for new discoveries. The GSI employs modern geophysical and geochemical techniques to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of these exploration programs. By conducting detailed geological surveys and exploration programs, the GSI contributes significantly to the development of Iran's mining industry and the exploitation of its mineral wealth. Moreover, the GSI's activities extend to environmental and groundwater studies. Iran’s arid climate and periodic droughts make groundwater resources critical. The GSI conducts hydrogeological surveys to assess groundwater availability and quality, which is vital for sustainable water resource management. Environmental monitoring by the GSI helps in identifying and mitigating the impacts of mining and industrial activities, thus promoting sustainable development.
Overall, Iran’s Geological Survey and Mapping efforts are essential for understanding the nation's geological heritage, managing its natural resources and safeguarding its environment. Through systematic mapping, exploration and research activities, the GSI contributes to the sustainable development and responsible stewardship of Iran’s geological wealth for the benefit of present and future generations. The integration of advanced technologies and comprehensive geological studies ensures that Iran can effectively utilize its natural resources while minimizing environmental impact.
Government Initiatives and Policies of Mineral Exploration
The Iranian government has taken substantial measures to foster mineral exploration and development as they recognize that this sector possesses the potential for driving economic growth and diversification. An important approach is implementing incentive programs, tax holidays and administrative reforms to attract both domestic and foreign funding into mining. One of such approaches is offering tax incentives and reductions on miners. The aim of these incentives is to reduce operational expenses while encouraging investment in exploration and development activities. In addition, the government has put in place measures aimed at simplifying and fast-tracking licensing processes for mining projects thereby making it easier for companies to obtain required permits hence start operations. Regulatory reforms have equally been part of the government’s policy. It involves issuance of clear guidelines regarding environmental protection as well as sustainable mining practices thus ensuring that mineral exploration and extraction are done responsibly with minimal environmental damage.
Collaborations between the state and industries are driving a high level of innovations in the exploration processes. These partnerships have mainly been brokered by the Iranian Mines and Mining Industries Development and Renovation Organization (IMIDRO). IMIDRO works together with domestic and foreign firms in the form of joint venture to develop the industry through sharing of best practices, technology, and capital. These collaborations help in providing an exchange of ideas and implementation of modern methodologies for exploration, which results in improvement of exploration projects’ performance and success rate. Also, the government has ensured that it put a lot emphasis on infrastructure development in the mining industry. These are the construction of transport systems like the roads, rails by which mining can be done and linked with the processing centers and port. There is an enhancement of physical facilities that decrease logistic issues and transport expenses so improving mining business and its profitability. Other stakeholders that are also being enlisted include the educational and research institutions in order to assist the mining sector. The government plays a key role of promoting the research activities, organizing the universities, research centers along with mining companies for betterment of working force. Thus, through education and training programs Iran supports its human capital with knowledge and skills required for efficient realization of complex exploration and mining activities.
Looking ahead, the future of mineral exploration in Iran appears promising, driven by emerging technologies, innovative exploration techniques and sustained investment in the mining sector. With careful planning, sound governance and a commitment to sustainability, Iran is poised to harness its rich geological resources, fostering economic growth and creating employment opportunities.
Among other promising trends in the development of mineral exploration in Iran in the future, one needs to mention the application of innovative technologies. Technological advancement, for instance, the introduction of remote sensing, use of drones and artificial intelligence (AI) in the exploration industry is transforming the key activities. Advanced technology such as remote sensing and drone services offer accurate imagery and data that help the geologists to determine the mineral deposits accurately and with elevation. The former is used to process geological data to forecast the location of the unexplored mineral deposits and to design the appropriate strategies for search into account.
Thus, apart from the existing technological progress, successful investment in the mining sector is necessary, which is the stated policy of Iran. It is assumed that during the following year both governmental and non-governmental organizations will continue investing in the upgrade of mining and mineral transportation facilities, improvements in the ore processing plants, and the best practices in mining. Such investments shall lead to enhancing efficiencies of the mining operations while at the same addressing concerns of Environmental and social sustainability. The other factor that has boosted the probability favorable outlook for mineral exploration in Iran is discovery factor. Covering the Middle of the Nearest continent, Iran’s geology is relatively young, complex and only partially explored and as such holds great potential in terms of undiscovered mineral resources. Altered exploration intentions backed by new tools and international partnerships are likely to discover more resource endowment, which is fundamental to growth.
Moreover, attention towards sustainable development strategy of Iran will contribute to the future prognosis of mining industry strategically. Thereby, following the international norms and standards and implementing the successful experiences proved in the world related to the environmental and community successful management in mineral industry, Iran can address the mining sector’s operation that would lead to the long-term sustainable economic growth and wellbeing of the communities and the environment preservation. Sustainability in the operation of mines should also facilitate the appeal to investors that focus on the ESG factors of the mining business. This trend corresponds to the trends observed around the world in sustainable and responsible investment, and places Iran in a competitive niche for mining with countries in this industry.
Future Outlook
Resources
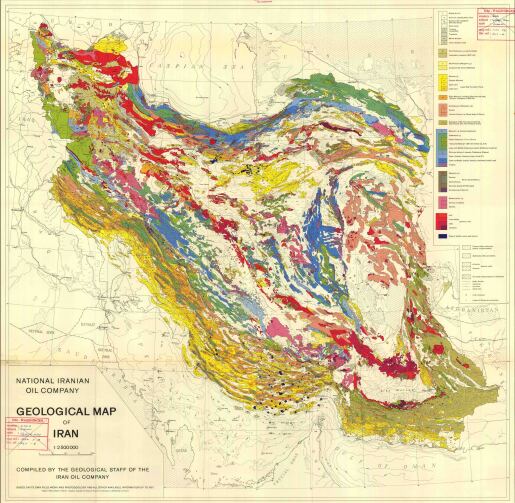
1. "Geological Map of Iran" Compiled by The Geological Staff of The Iran Oil Company and Published by National Iranian Oil Company, 1957.
2. Alavi, M.; "Tectonics of the Zagros Orogenic Belt of Iran: New Data and Interpretations", Tectonophysics, 229(3-4), pp. 211-38, 1994.
3. Allen, M. B.; Ghassemi, M. R.; Shahrabi, M.; Qorashi, M.; "Accommodation of Late Oblique Shortening in the Alborz Range, Northern Iran ", Journal of Structural Geology, 25(5), pp. 659-72, 2003.
4. Aghanabati, A.; Geology of Iran, Ministry of Industry and Mines, Geological Survey of Iran, 2004.
5. United States Geological Survey (USGS), Iran Minerals Map 2, https://usgs.gov, 2016.
6. Hassanpour, M.; Atapour, H.; "Mineral Resources of Iran", In: A. Pohl (Ed.) Handbook of Mineral Exploration and Ore Petrology, Springer, pp. 469-85, 2019.
7. Iranian Mines and Mining Industries Development and Renovation Organization (IMIDRO), "Annual Report", Tehran, Iran, 2021.
Iran's Geological Survey and Mapping efforts are essential for understanding, utilizing, and preserving the country's rich geological heritage. These initiatives play a crucial role in assessing natural resources, managing environmental risks and guiding sustainable development strategies across various sectors of the economy.
The Geological Survey of Iran (GSI) serves as the primary institution responsible for conducting geological surveys, mapping and research activities throughout the country. Established in 1958, the GSI has been instrumental in documenting Iran's geological features, mineral resources and seismic hazards. The institution's mandate includes geological mapping, mineral exploration, groundwater assessment and environmental monitoring.
The GSI does geological mapping which is a basic activity. When detailed, these maps give vital data about the distribution, nature and age of rock formations, structural features and mineral deposits. These maps are extremely helpful in mineral exploration, land use planning and development works. The GSI makes use of advanced technologies such as remote sensing, GIS and geophysical surveys during the preparation of accurate and comprehensive geological maps. Apart from mapping, GSI also conducts extensive mineral exploration programs. These programs target identifying Iran’s mineral wealth including precious metals, base metals, industrial minerals as well as energy resources. With its systematic surveys and exploratory drilling efforts; GSI has discovered numerous important mineral deposits contributing to the country’s economic growth.
Groundwater assessment is another critical area of focus for the GSI. Because Iran has an arid and semi-arid climate, it is necessary to manage water resources. The GSI also carries out hydrological research to assess the volume and quality of underground water as well as carry out underground water level monitoring and identification of aquifers. This knowledge is important in ensuring that water use is sustainable particularly in agriculture and urban areas. Environmental monitoring and assessment are also vital activities for the GSI. Iran has a range of environmental problems such as soil erosion, desertification, pollution among others. The institute monitors these challenges hence giving information which helps in protecting environment and managing natural resources. Therefore, through understanding geological and environmental controls, the GSI assists in hazard mitigation as well as sustainable development.
Geological Survey of Iran (GSI) and Mapping
Conclusion
Iran's rich geological survey and mineral exploration efforts hold the promise of unlocking immense wealth and prosperity for the nation. With its diverse geological landscape, abundant mineral resources and concerted efforts to promote exploration and development, Iran is well-positioned to emerge as a leading player in the global mining industry. By harnessing the power of science, technology, and innovation, Iran can unlock the full potential of its geological treasures, paving the way for a brighter future for generations to come.
Iran will continue offering several opportunities of mineral exploration in the future due to technology advancement, better exploration methods and the continuous investment in the mining industry. The government of Iran has a great potential to develop the country’s wealth by following correct business models of governance and embracing sustainable development to transform the abundance geological resources into the economic growth factors and job creations. Also, it is loyal to further invest its capital in the mining sector for future development of the sector. Government and investors are likely to spend on revamping processing and utility structures, improving on the techniques of mining and establishing environmentally friendly mining technologies. As a result, the efficiency of mining operations will improve and the levels of the negative influence on the environment and communities will decrease. Moreover, due to the rich geological zones that Iran boasts, the country has a very rich potential for the discovery of other mineral sources. It can therefore be expected that through more systematic and scientific screening activities and employment of sophisticated techniques intertwined with international partnerships, new assets capable of supporting the economy would be put to light. When the legislative and executive branches act in accordance with standards accepted all over the world Iran may look through the experience of other countries lessons which explains that mining works may bring long-term benefit and may not be at the cost of negative impact on population and environment. Such a strategic direction defines Iran’s role as a contender for the dominance of the global mining industry and its willingness to face and seize the opportunities of the future.
The work done by the GSI contributes significantly to policy formulation for economic development based on sound science underpinning effective environmental management in Iran. The activities carried out by the GSI include detailed geologic surveys; mapping of every part of Iran’s territory; and national geologic database establishment to ensure sustainable utilization of geological resources with a view to preservation for future generations.
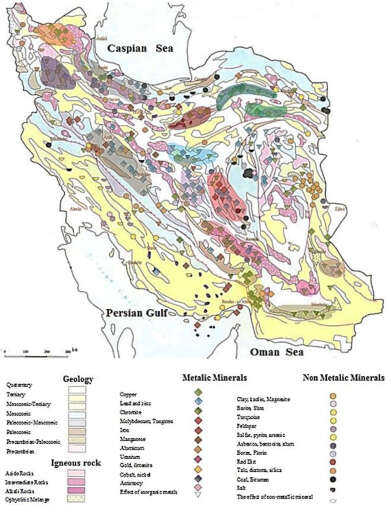
The mineral distribution map of Iran
Written by Zamin Kavan Company (ZKC)
which is a subsidiary of Kimia Holding, specializes in the exploration, exploitation, and processing of diverse mineral resources. It is prepared to offer technical and engineering services to stakeholders in the mining industry, encompassing consultation, design, and implementation phases. Leveraging state-of-the-art technologies and expert teams, the company has successfully completed numerous projects, significantly contributing to the development of the mining industry in the country.





